By now, you must have deleted a file from your computer system by mistake, and when you heard about it, it was as if the world came to an end without those files! In such situations, what is your reaction other than expressing regret and anger? The good news is that with Microsoft’s Deleted Files recovery tool, you can make up for some of this disaster, you just have to take some time and be careful to recover the lost files. In this article, we want to teach you step by step How to Recover Deleted Files on Windows 10? with Windows File Recovery utility to recover deleted files in Windows.
Microsoft’s Windows File Recovery tool is used to recover deleted files from hard drives, SD cards, USB drives, and other storage spaces.
How to install Windows file Recovery tool?
Windows File Recovery is a command line interface provided by Microsoft for free for windows 8 and windows 10 users. Since it is free of cost you can Download and install the Windows File Recovery tool from the Microsoft Store. You can install the tool on your system to recover deleted files by going to the Microsoft Store and searching for Windows File Recovery.

After installation, open your system start menu and type File Recovery in the search box as shown below. When the Windows File Recovery shortcut is provided, click Yes.
In this step you will see the “Command Prompt” window with “Administrator” access, this step is exactly where the commands to recover deleted files will be executed.
You can also use other command line environments such as Windows Terminal and PowerShell, but first make sure you are logged in with Administrator access. To do this, in the Start menu of the system, right-click on the desired program and then select Run as Administrator.
How to Recover deleted Files on Windows 10?
To use this tool, run the “winfr” command, specify the drive you want to search and the recovery location. Setup keys and how to search must also be specified. Note that you must save the deleted file to another drive after recovery.
This is the basic format you need to type:
winfr source-drive: destination-folder [/switches]
- winfr is the command for Windows File Recovery
- Source Drive: Mention the location of the disk or volume you want to recover.
- Destination: Verify a location to save the recovered files.
- Switches: If you want to recover deleted files from SD card (Fat32 File system) use /x but if your file system is NTFS use the /r. If you don’t understand here, don’t worry I explain everything futher.
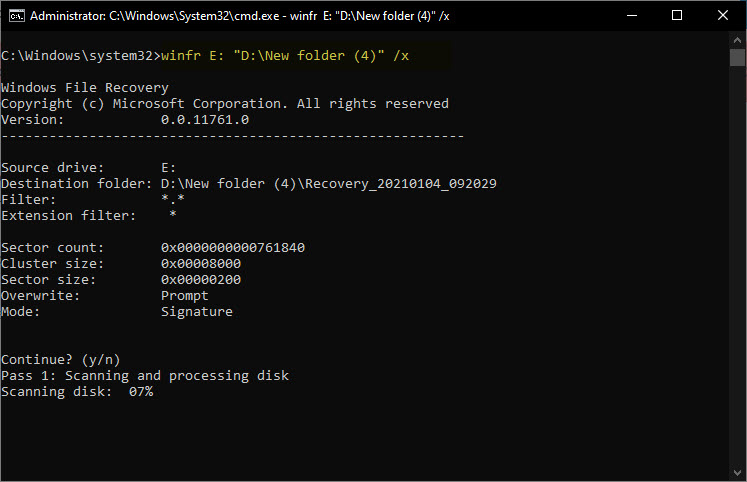
So this winfr source-drive: destination-folder [/switches] = winfr E: “D:\New folder (4)” /r
After you run this command, the tool will automatically create a directory called Recovery (with date and time) on the destination drive.
Which Mode should be used to Recover Deleted Files?
Before proceeding, you must specify the Mode for scanning the deleted file, for which there are three modes:
- Default
- Segment
- Signature
The default mode is the fastest mode, while the segment mode is the most similar mode but slower and of course the most complete mode. Signature mode can also be selected for different files (depending on the type of search). This third mode supports ASF, JPEG, MP3, MPEG, PDF, PNG and ZIP files. (By searching zip files, you can find Office documents stored in formats such as DOCX, XLSX, and PPTX).
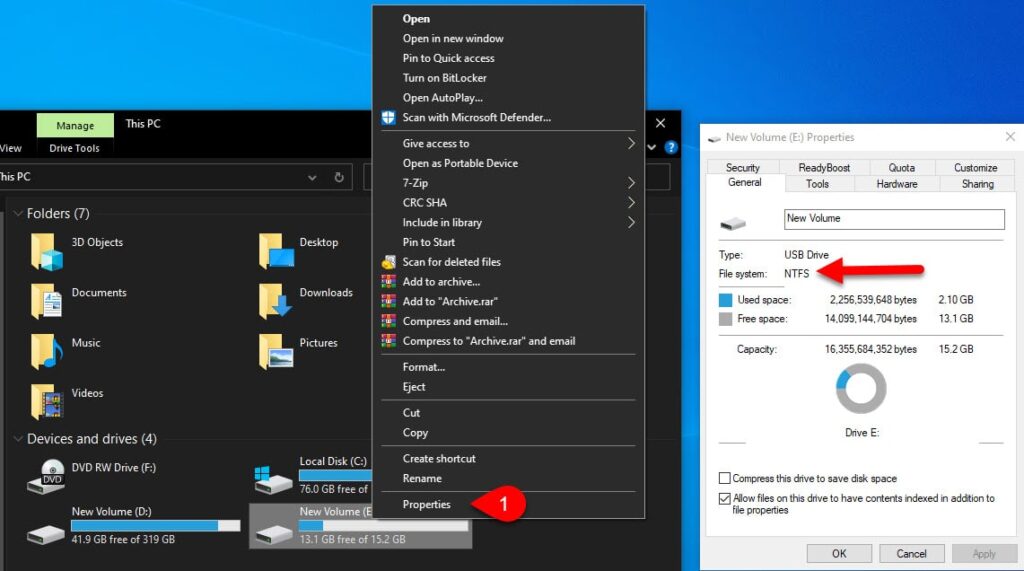
You need to be aware of the process by which the drive is scanned. To discover this, open “File Explorer” and right-click on the drive below “This PC” and then select “Properties”, here you will see the type of drive format in the General section.
Here you have to use different modes, such as:
Do you want to recover the deleted file in “NTFS” format (Windows 10 default format).
- If you are scanning the NTFS drive in another state, for example if you have already deleted the file, formatted the drive or dealt with the damaged drive, try the segment mode first and then the signature mode.
- If you want to find the file stored on the FAT, exFAT or ReFS drive, use Signature mode. Default and segment modes are only compatible with NTFS file formats.
Also, if you have doubts about choosing the desired mode, it is better to start with the default mode and if the default mode does not work, try the signer and segment modes.
To put them in simple words, for USB flash Drive use the /r, for SD card from your mobile use the /x.
From Here on the next steps are a bit pro, if you don’t like quit reading here.
How to Recover a File by default?
To use the default mode, do the following:
- Use n document.docx/ to search for a file named docx. You can also specify the full path to the file, for example / n \Users \Abbas\Documents\document.docx
- To search for all the files in the Documents folder, for example, if your username is Abbas, use the “/ n \Users\Abbas\Documents” path.
- You can also use the “. *” Search help. For example, by writing the following phrase, all the files in the “Documents” folder with the extension “docx.” Found:
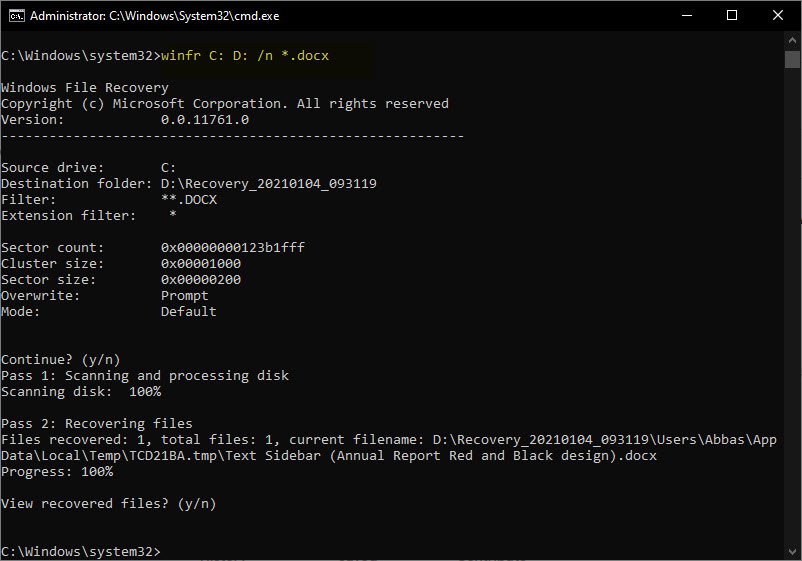
n \Users\Abbas\Documents\*.docx/Now let’s summarize all this. To search for files with the DOCX extension on drive C and copy them to drive D, run this command:
winfr C: D: /n *.docxYou must also type the letter y and continue.
As mentioned, the recovered files will be found in a directory called _Recovery (with time and date) in the destination drive path (specified on the command line).
Run the following command to find all files containing specific words such as “Project”:
winfr C: D: /n *project*You can also specify multiple searches with multiple n / switches, so run this command to find all Word, Excel, and PowerPoint files:
winfr C: D: /n *.docx /n*.xlsx /n *.pptxUse this command to search for a specific file, for example named important_document.pdf, in the Users, Abbas, Documents folder on drive C, which you then saved to drive D:
winfr C: D: /n \Users\Abbas\Documents\important_document.pdfHow to Recover Deleted Windows files in segment mode?
The segment mode is almost the same as the default mode. Use “r /” plus n / to use this mode, which examines file storage sections. In other words, you can create segment state recovery commands in the same way as the default state commands, you just need to add r /. For example, in order to recover all deleted MP3 files from computer C drive and save them to D drive, you must run the following command:
winfr C: D: /r /n *.mp3So if you do not find the file you are looking for by default, add / r and try again.
Recover deleted Windows files with Signature mode
This mode works a little differently. In fact, this mode scans all types of files so it can only find certain types of deleted files. To use Signature Mode, you can use x / to specify Signature Mode, and for the list of file type groups, y / is the solution.
The following is a list of supported file types and groups that have been sorted from Microsoft documents:
- ASF: wma wmv, asf files
- JPEG: jpg, jpeg, jpe, jif, jfif, jfi files
- MP3: mp3 files
- MPEG: mpeg, mp4, mpg, m4a, m4v, m4b, m4r, mov, 3gp, qt files
- PDF: pdf files
- PNG: png files
- ZIP: zip files, docx, xlsx, pptx, odt, ods, odp, odg, odi, odf, odc, odm, ott, otg, otp, ots, otc, oti, otf, oth
Note that the ZIP group contains compressed files plus Microsoft Office and OpenDocument documents.
You can also compile this list whenever you want by executing the following command:
#/ winfrIf you also want to look for deleted files on drive E: Run this command for photos in JPEG format and save them to drive D:
winfr E: D: /x /y:JPEGWhile you can specify multiple file groups by separating them by space, so if you want to find jpg, pdf and word documents, run the following command:
winfr E: D: /x /y:JPEG,PDF,ZIPMore Tips with winfr to Recover Deleted Windows Files
By following the steps mentioned above, you can recover deleted Windows files. For newer basics as shown below, you just need to execute the commands. This will provide additional advanced options that you can view by running! / Winfr!
winfr or ?/ winfr Here are the results in CMD.
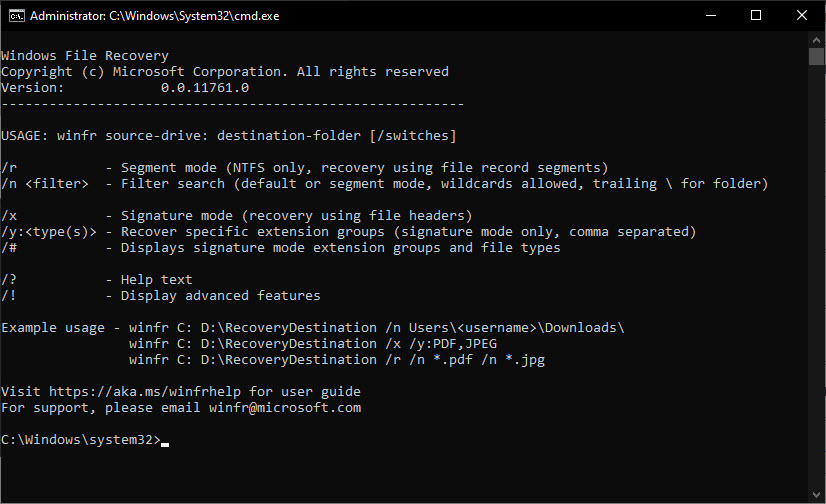
C:\Windows\system32>winfr /?
Windows File Recovery
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved
Version: 0.0.11761.0
----------------------------------------------------------
USAGE: winfr source-drive: destination-folder [/switches]
/r - Segment mode (NTFS only, recovery using file record segments)
/n <filter> - Filter search (default or segment mode, wildcards allowed, trailing \ for folder)
/x - Signature mode (recovery using file headers)
/y:<type(s)> - Recover specific extension groups (signature mode only, comma separated)
/# - Displays signature mode extension groups and file types
/? - Help text
/! - Display advanced features
Example usage - winfr C: D:\RecoveryDestination /n Users\<username>\Downloads\
winfr C: D:\RecoveryDestination /x /y:PDF,JPEG
winfr C: D:\RecoveryDestination /r /n *.pdf /n *.jpg
Visit https://aka.ms/winfrhelp for user guide
For support, please email [email protected]
C:\Windows\system32>Winfr /!
Windows File Recovery
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved
Version: 0.0.11761.0
----------------------------------------------------------
USAGE: winfr source-drive: destination-folder [/switches]
/p:<folder> - Specify recovery log destination (default: destination folder)
/a - Accepts all user prompts
/u - Recover non-deleted files (default/segment mode only)
/k - Recover system files (default/segment mode only)
/o:<a|n|b> - Overwrite (a)lways, (n)ever or keep (b)oth always (default/segment mode only)
/g - Recover files without primary data stream (default: false, default/segment mode only)
/e - Disable extension exclusion list (default/segment mode only)
/e:<extension> - Disable specific extension(s) (default extension list no longer applies) (default/segment mode only)
/s:<sectors> - Number of sectors in volume (segment/signature mode only)
/b:<bytes> - Number of bytes in cluster (segment/signature mode only)
/f:<sector> - First sector to scan (segment/signature mode only)
C:\Windows\system32>Also Read:
- How to Reset Forgotten Windows 10 Password?
- How to Encrypt Files on Windows 10?
- How to Install Android 10 on Android Studio on Windows?